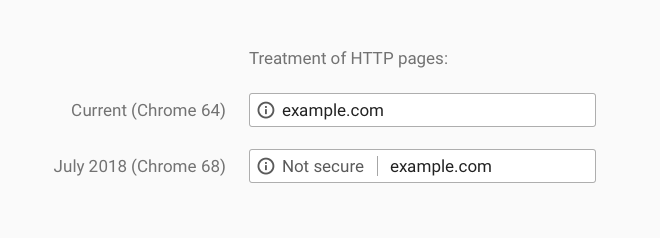
HTTP tag in Chrome browser
According to Emily Schechter, Chrome Security Product Manager, since July, Google Chrome will begin marking all sites that do not have HTTPS tags as unsafe. At this time, Chrome displays a neutral information icon in the address bar of the site, but when a new version of Chrome is released, the browser will alert users with an additional message.
Over the past few years, Google has made great efforts to make as many websites as possible use the HTTPS tag. In addition, by gradually marking more and more HTTP pages unsafe, Google has helped users understand that HTTP sites are not secure.
Why is HTTP different from HTTPS?
Both of these protocols are intended for the transmission of information (documents, pictures, files, etc.) over the Internet. The main difference between them is the letter “S” representing the word “Secure”.
This means that the HTTPS protocol has the same purpose as HTTP, but HTTPS also takes care of encrypting and decrypting the data being transferred.
HTTPS encryption protects the channel between your browser and the site you visit. This ensures that no one can interfere and change traffic or see what you do. In addition to HTTPS encryption, anyone with access to your router or Internet service provider could take over and correct the information sent to the site or insert malicious software.
Using the HTTPS tag is getting easier. You can use automated services such as Let’s Encrypt or Google’s Lighthouse Tool, which includes site-to-site HTTPS tools.
The Chrome team says that the appearance of this message was influenced by the increased use of HTTPS. 81 of the 100 most popular websites have the HTTPS tag by default and most of the Chrome traffic is already encrypted.
Interested? Let's discuss your project
Call us or write us an email and we will arrange a meeting, during which we will discuss your project and our ideas for you.